Comprehensive Guide to Inline Skate Wheels

- Wheel size: Influences speed and manoeuvrability.
- Durometer: Wheel hardness – impacts speed and vibration absorption.
- Rebound: The speed at which the wheel returns to its initial shape after compression.
- Grip: Determines the wheel's ability to adhere to the surface.
- Wheel profile: Influences speed and stability.
Overview
Overview
Which Inline Skate Wheels Should I Opt For?

Making a selection of wheels for inline skates is simplified when you understand which ones suit your skating style.
Whatever your preferred style of inline skating, it's vital to focus on the size and hardness of the wheels and align these with the surfaces you'll be skating on.
| Inline Skating Style | Properties | Size Range / Hardness Range |
| Fitness Skate Wheels |
Smooth roll Power transfer
|
80-110 mm 80A-88A |
| Freeskate Wheels |
Agile and fast |
75-110 mm 84A-88A |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels |
Stable and shock-absorbing Small size Flat or round profiles |
55-80 mm 88A-95A |
| Roller Hockey Wheels |
Agile and grippy Good acceleration Some are indoors-specific |
65-84 mm 72-84A
|
| Speed Skate Wheels |
Maximum speed Indoor / rinks / outdoor / roads |
100 mm-125 mm 83A-90A |
Inline Skate Wheels Compatibility

Inline skate wheels typically feature a width of 24 mm, simplifying the process of identifying compatible wheels for your skates. Any wheel smaller than or equal to the maximum diameter specified for your rollerblade frames can be installed on them.
Understanding factors such as hardness, rebound, grip, and profile will not only help you choose wheels that fit but also enhance your inline skates' performance.
Read further for more insights, or explore our collection:
Diameter: The Size of Inline Skate Wheels
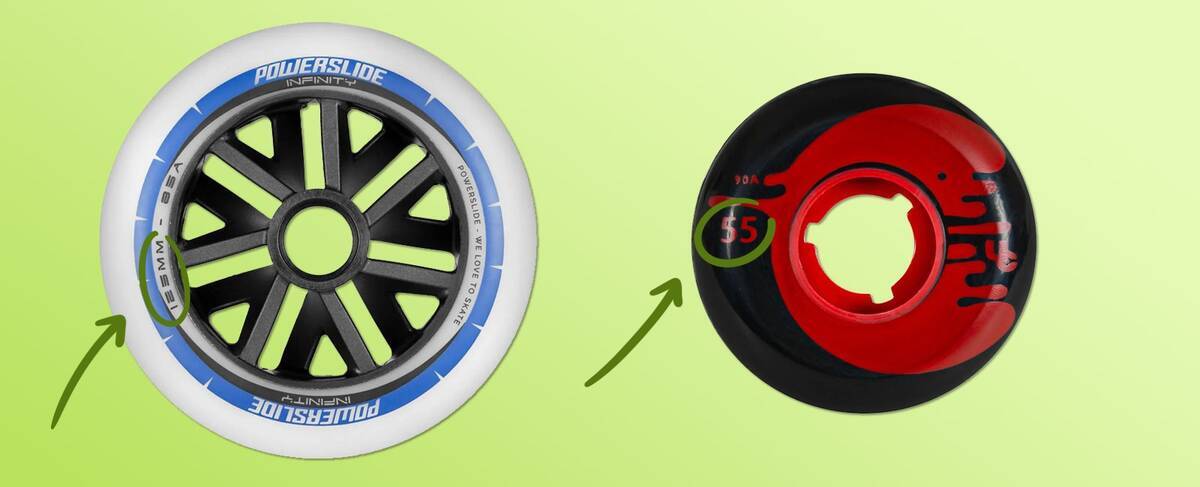

Measured in millimetres (mm), the diameter of inline skate wheels is often marked on the side of the wheel. If uncertain, you can measure the diameter yourself.
The diameter exerts considerable influence on how inline skate wheels perform, affecting aspects such as acceleration, speed, manoeuvrability, and stability.
Below is how the wheel diameter affects your skates' performance:
- Smaller diameter: Offers better acceleration and control.
- Larger diameter: Provides higher speeds and improved stability.
Each style of skating has different recommended wheel diameters. The following chart provides general advice for each skating style:
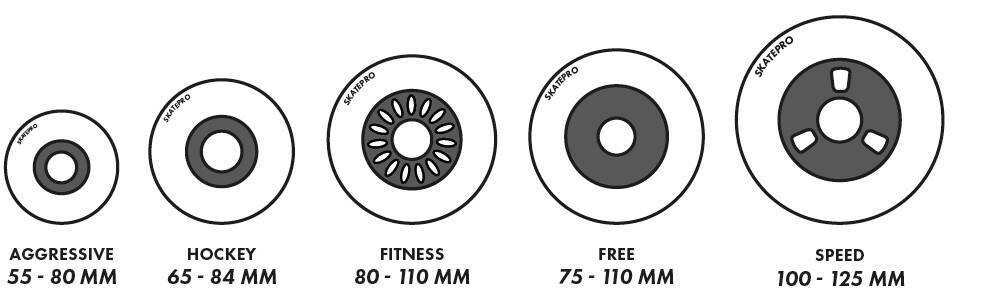
Inline Skate Wheels Size Chart
| Inline Skating Style | Size Range |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels | 55-80 mm |
| Roller Hockey Wheels | 65-84 mm |
| Fitness Skate Wheels | 80-110 mm |
| Freeskate Wheels | 75-110 mm |
| Speed Skate Wheels | 100-125 mm |
Hardness of Wheels - Durometer

The hardness of rollerblade wheels is often gauged using durometer, a standard measurement method for materials like rubber and plastics. Rollerblade durometer ratings typically use the A-scale. You’ll notice a number followed by an A (e.g., 82A), where a higher number denotes harder wheels.
The A-scale facilitates easy comparison of wheel hardness, and the durometer rating is usually printed on the wheel side.
Optimal wheel hardness varies by skating style. The chart below provides general suggestions for selecting the appropriate durometer for different inline skating styles:
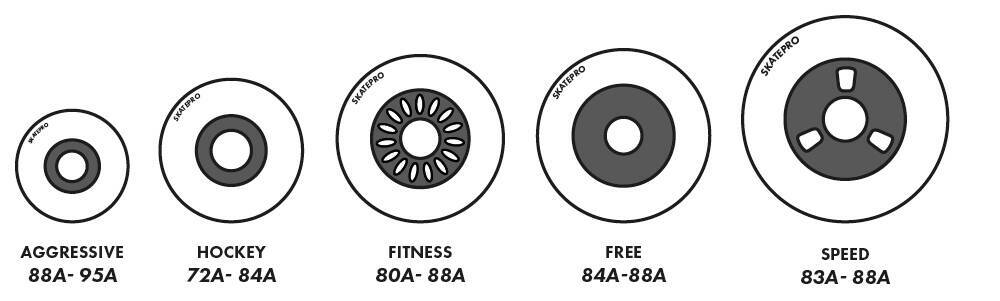
Inline Skate Wheels Hardness Chart
| Inline Skating Style | Hardness Range |
| Aggressive Skate Wheels | 88A-95A |
| Roller Hockey Wheels | 72A-84A |
| Fitness Skate Wheels | 80A-88A |
| Freeskate Wheels | 84A-88A |
| Speed Skate Wheels | 83A-90A |
The surface and conditions under which your wheels perform depend heavily on their hardness. Consider the wheels' hardness when making a purchase as it greatly influences your skates' functionality.
Inline Skate Wheels: Hard vs. Soft
Understanding how hardness affects performance is essential, particularly when faced with choosing between softer and harder wheels.
Implications of wheel hardness on rollerblade performance:
Benefits of harder wheels- Faster speeds
- Increased durability
- Reduced grip
- Lower vibration absorption
- Enhanced grip
- More shock absorption
- Slower speed
- Reduced durability
The basic premise with inline skate wheels is that softer variants provide increased vibration absorption and better surface adhesion, while harder wheels offer reduced absorption and grip.
Alternative Hardness Metrics
Some brands utilise the footprint scale to assess rollerblade wheel hardness. Here’s how it compares to the A-scale:
- F0 - roughly equivalent to 88A
- F1 - roughly equivalent to 85A
- F2 - roughly equivalent to 84A
- F3 - roughly equivalent to 83A
Rebound Characteristics of Inline Skate Wheels
Rebound refers to a wheel's capability to rapidly rebound to its original form after compression. As you skate, each exertion compresses the wheel; a wheel with high rebound efficiency accelerates back to shape, boosting speed. In contrast, a low-rebound wheel absorbs more energy from each stride, translating to less speed. Therefore, wheel rebound plays a crucial role in your speed.
Typically, high-quality wheels exhibit a high rebound, often marked as SHR urethane by manufacturers, meaning Super High Rebound. While there's no universal method for assessing rebound, affordable wheels generally have a lower rebound, whereas higher-end wheels from well-regarded brands exhibit superior rebound.
Inline Skate Wheels: Grip
The grip of inline skate wheels is largely determined by the polyurethane (PU) formula used for the rubber. Wheel hardness significantly impacts grip.
The relation between wheel hardness and grip is as follows:
- Softer wheels: Increased grip.
- Harder wheels: Reduced grip.
The performance of a specific wheel's grip largely depends on the surface encountered. Slippery surfaces like indoor rinks or skateparks demand enhanced grip to prevent slipping, while rougher terrains like asphalt make grip a lesser concern.
Therefore, when skating on rough surfaces, harder wheels can be used without worrying about unwanted slip incidents.
The Profile of Inline Skate Wheels
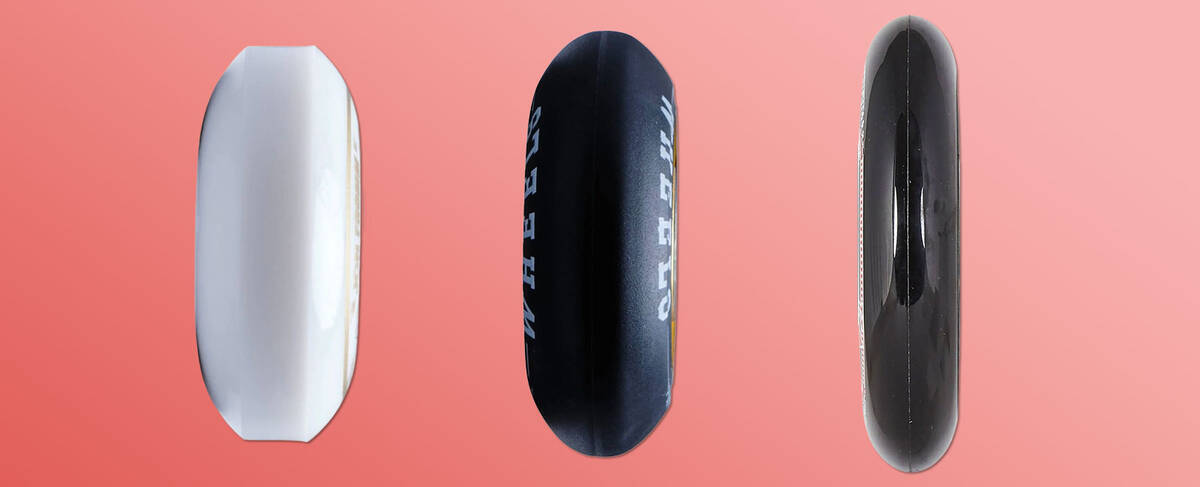

Inline skate wheels feature diverse profiles which range from flat to sharp. The profile governs the contact width between the wheel and surface. A flat profile has a larger contact area, whereas a sharp wheel has a smaller one.
Sharp wheels serve multiple skating styles, such as fitness and speed skating. They minimise friction and rolling resistance due to their narrow contact patch, making them very effective. The sharp wheel profile is popular owing to its versatility and attractive speed properties.
Flat wheels are exclusively tailored for aggressive skating. Though they lack speed, they provide stability advantageous for trick landings.
Rounded wheels find use in freeskating and aggressive skating alike. In aggressive skating, they often feature in flat setups where the rounded edges help avoid wheel bites. Easier to manipulate than sharp wheels, they are ideal for beginners for their forgiving nature.
Understanding Hubs in Inline Skate Wheels

The hub constitutes the wheel's core, holding the bearings in place. Typically crafted from hard plastic or aluminium, the hub provides a sturdy base. Aluminium hubs are generally heavier (design-dependent) but offer more impact resistance and durability compared to plastic ones.
Inline skate wheel hubs can categorically be described as follows:
- Solid core: Provides strength but increases weight.
- Spoked core: Offers reduced weight, albeit with less durability.
- Hollow core: Balances low weight with durability.
For optimal efficiency, inline skate wheels should balance strength, durability, and lightness. Lighter wheels demand less effort in lifting skates, thereby conserving energy and minimising fatigue.
Caring for Your Inline Skate Wheels
To ensure your wheels last as long as possible, a consistent maintenance routine is advisable. As wheels generally wear out quicker than other skate parts, prudent management can lead to cost savings. A regular schedule of wheel rotation can extend their lifespan and maintain peak skate performance.
A typical wear pattern for inline skate wheels causes the centre to shift outward, forming a slanted edge on the inner side. This pattern negatively impacts your technique, signalling the need for wheel rotation.
```Ensuring rollerblade wheels retain their consistent shape can be achieved through proper rotation. If you're unsure about the process, our detailed guide can assist you:
Wondering if it's time to replace the wheels on your inline skates? Consult our guide for clarity:
Assistance for mounting wheels is just a click away:
Seeking advice on the overall upkeep of inline skates? Our comprehensive online guide is loaded with valuable tips:
... What About Bearings?
Discover all you need to know about wheel bearings in our exclusive guides:
If your ride isn't as smooth, it may be time to clean and lubricate your bearings thoroughly: