Scooter Forks Purchasing Guide
Prepare yourself for our extensive guide to selecting stunt scooter forks. We will discuss all the crucial factors to take into account before choosing a new freestyle scooter fork. These include compatibility, wheel sizes, wheel offset, and other considerations.
A well-adjusted stunt scooter requires an exceptional fork. Scooter forks are crucial as they hold the front wheel of your scooter, and the specific features of your fork determine the wheel sizes you can fit, both in terms of wheel width and diameter. Stay tuned for some informative advice on stunt scooter forks!
Overview
Essentials of Scooter Forks

The fork goes through both the headset and the headtube of your deck. The front wheel mounts onto the fork, and above the fork, you attach the compression system, clamps, and bars. Your fork greatly affects your setup because it dictates the wheel sizes you can use.
Nowadays, most scooter forks are crafted from a single piece of aluminium, enhanced through different heat treatments. Threaded scooter forks made of steel, once widespread, are now outdated due to their decreased durability and heavier weight.
Scooter forks compatible with SCS, HIC, and IHC have an integrated starnut within the fork tube. The compression bolt fits into this starnut during the installation of the compression system.
ICS setups differ as the starnut in ICS is inside the bar, and the compression bolt is installed through the underside of the fork before the wheel is attached. If there's any uncertainty about the compression system in use, it's wise to review our detailed guide:
When choosing a new scooter front fork, important considerations are weight, wheel size, wheel offset, and compression. This guide will explore these topics in depth.
We consistently provide top-quality scooter forks from leading industry brands, likely including one to fit your requirements. If you're ready to decide, explore our range of high-quality forks for stunt scooters:
Scooter Forks and Wheel Dimensions

When selecting a new fork for your scooter, always ensure it matches with the wheels. Confirm wheel size compatibility in terms of both diameter and width. Make sure the wheel diameter doesn't exceed the maximum specified by the fork, and that the wheel hub's width is equal to or less than the wheel size indicated by the fork.
Wheel Diameter
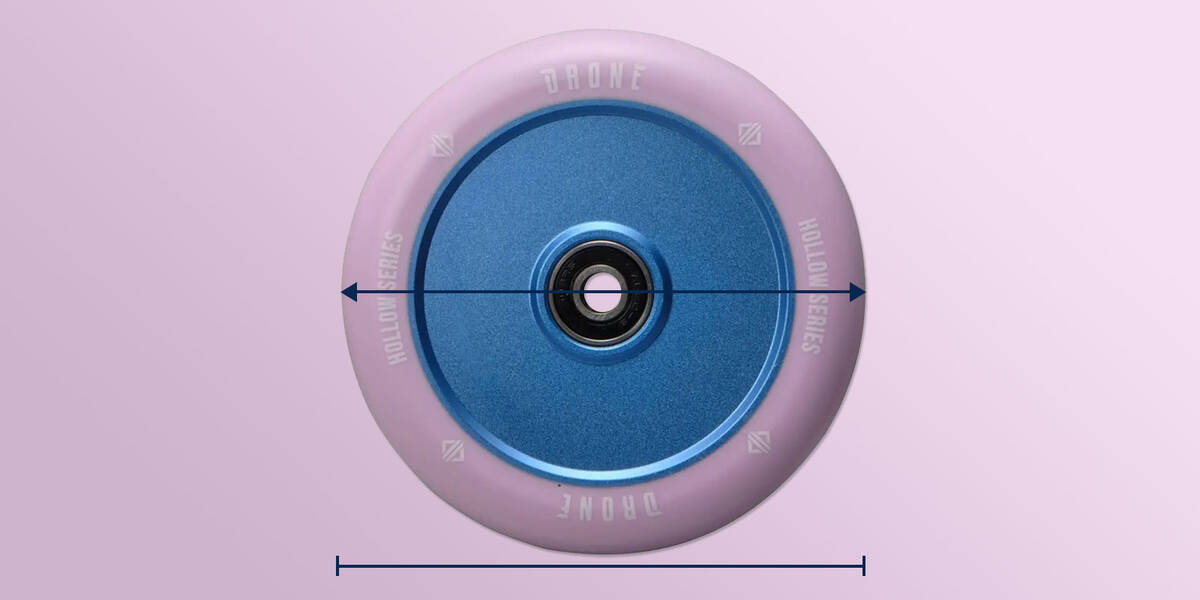
Typically, most scooter forks accommodate wheel diameters of 110 mm, the standard size. However, numerous forks can fit scooter wheels up to 125 mm. Confirm that your wheels don't surpass the fork's limit, and you'll be prepared.
Illustratively, if using wheels of 115 mm diameter, verifying that your fork can fit such or larger wheels is crucial.
Wheel Core Width
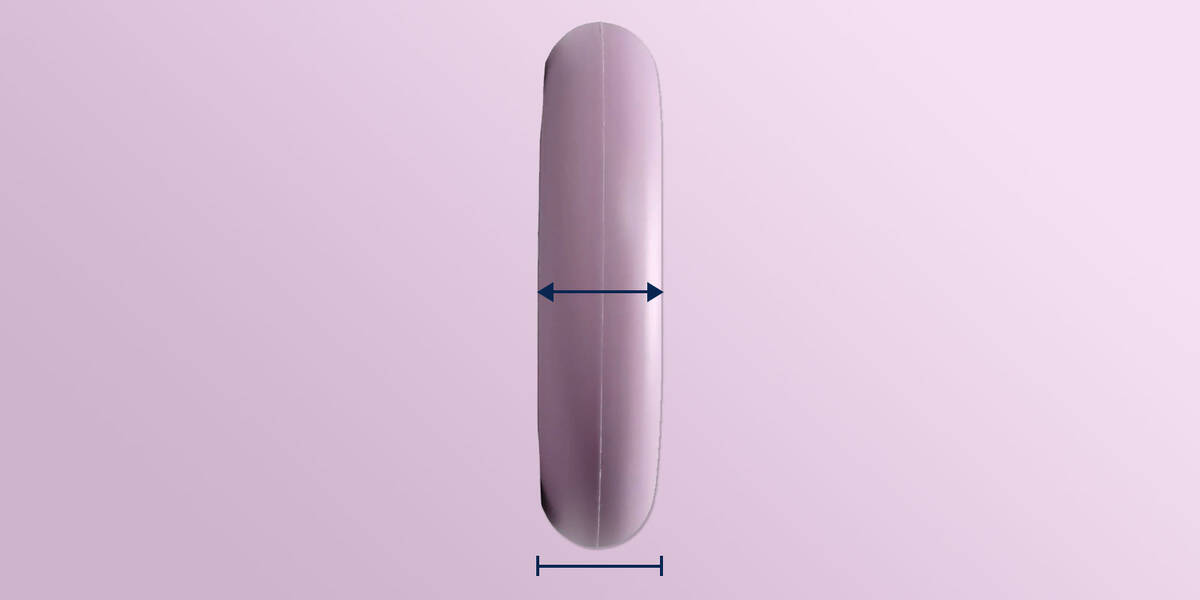
Scooter forks are built to fit wheels of certain widths, usually from 24 to 30 mm. In between, scooter wheels often feature widths of 26 and 28 mm.
Frequently, scooter forks are supplied with spacers, allowing a fork made for 30 mm wide wheels to also fit 24, 26, and 28 mm wheels when the correct spacers are used.
Wheels narrower than a scooter fork's maximum wheel hub width can be mounted, but wider wheels (e.g., a 30 mm wide wheel for a 24 mm fork) won't fit.
Fork Axle Diameter and Length

The common scooter wheel axles have an 8 mm diameter, though some forks also accept scooter wheel axles at a 12 mm diameter. The standard bearing size for scooters is the 608, compatible with 8 mm axles. Forks that suit the 12 standard often come with 8 mm adapters so you can utilise the usual 8 mm axles.
To determine the proper axle length, measure the width of your scooter fork. Select an axle that is at least as long as the fork's width, measured from its outer sides.
Understanding 12 Standard Scooter Forks
12STD scooter forks are made for wheel axles with a 12 mm diameter. For such an axle, you will need the 6001 bearing size.
A 12-standard stunt scooter setup usually includes larger and broader wheels. Generally, one can anticipate that 12STD setups will deliver increased speed, stability, and robustness, albeit alongside additional weight and reduced agility.
Many 12 standard forks feature spacers making it feasible to use 8 mm axles and standard 608 bearings on the fork.
Transitioning to 12STD requires recognising that, aside from the 12STD fork, wheels suitable for 6001 bearings and a deck compatible with larger wheels and axles are necessary. You can discover what's needed in our collection:
Wheel Alignment on Pro Scooter Forks

Wheel offset, measured in millimetres, represents the distance between the fork's turning axis centre and the wheel axle. Known also as the rake, the offset indicates the wheel's position relative to the fork.
Offset has a significant impact on your scooter's stability and manoeuvrability as it alters the wheelbase, or the distance between the front and rear wheels.
A 10 mm wheel offset is typical, enhancing overall stability and control, simplifying steering of the scooter.
Zero-offset forks offer greater agility. With zero offset, the front wheel comes closer to the rider, adopting higher agility and responsiveness. Zero-offset forks ease nose manuals since the feet are closer to the ground, assisting balance. A broader wheel surface available for jamming facilitates executing foot jams.
Scooter Forks & Compression Mechanisms
SCS and HIC compression use similar forks, integrating a starnut within the fork tube for a compression bolt. The key divergence is in the compression components around the fork: SCS uses an SCS clamp, while HIC employs an HIC shim.
IHC compression forks come with a narrower fork tube, ideal for those who wish to minimise setup weight. Generally, IHC forks are the lightest available for scooters.
- SCS Scooter Forks: Standard & oversized bars without slits and oversized or standard SCS clamps
- HIC Scooter Forks: Oversized bars with slits and non-SCS oversized clamps
- IHC Scooter Forks: Standard bars and non-SCS standard clamps
For ICS and ICS-10 compatible forks, the compression bolt is installed from beneath and fits a starnut within the bars. ICS setups, uncommon in custom-built scooters, are notable for being exceptionally lightweight compared to other systems.
If compatibility concerns between different forks arise, consult with these guides:
